Art by Allison Horst
some guiding principles, tools, and resources on how to write clean and readable code
Writing clean, easily readable, and reproducible code is just as important as understanding any of the data visualization tools you’ll learn in this class. Now is the time to practice this skill so that you can take your beautiful code and styling skills with you into the workforce!
Stick to these standards (as suggested by The tidyverse style guide) whenever possible:
my_datamy-script.R
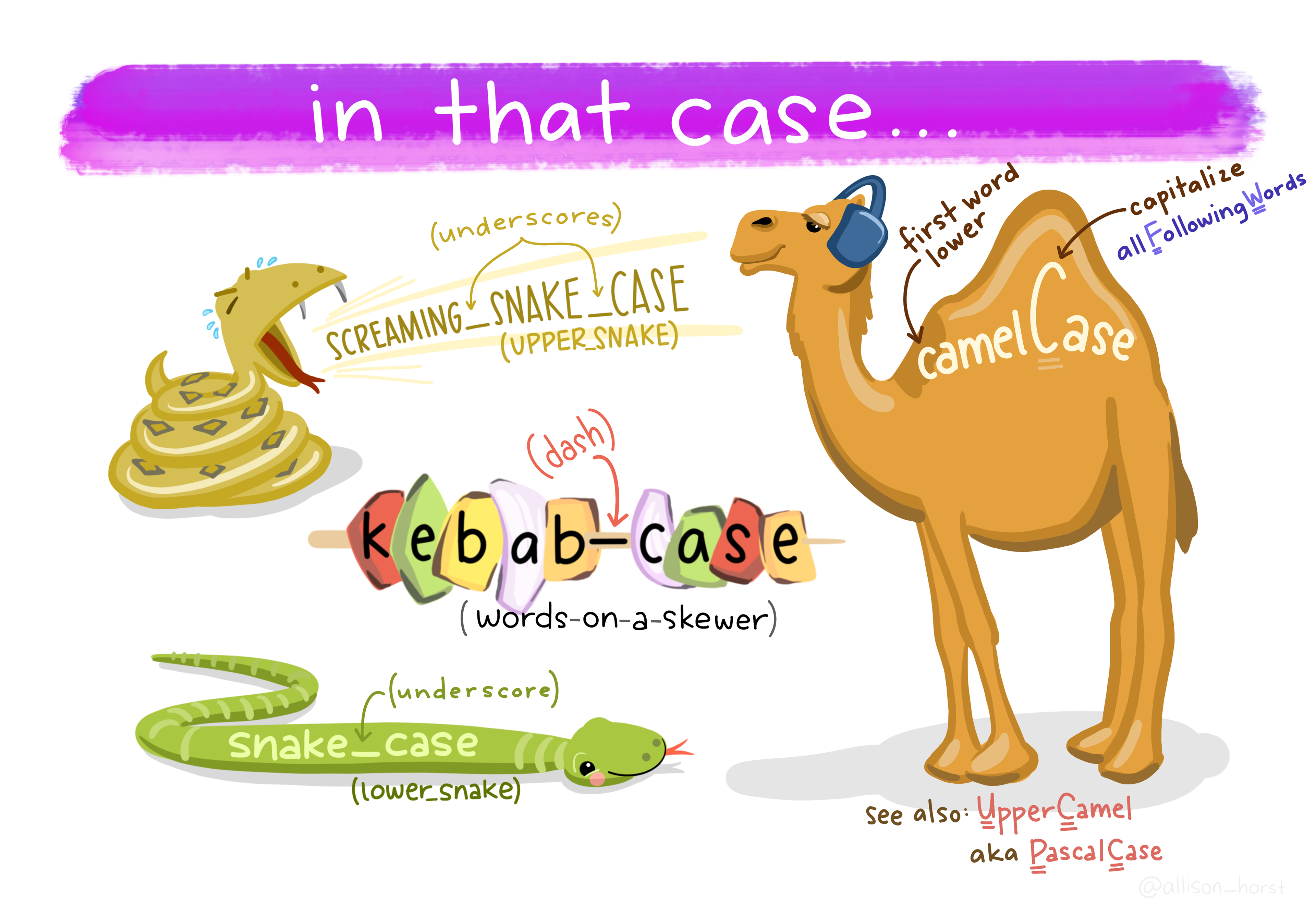
Art by Allison Horst
==, +, -, <-, etc) – for example:::, :::, $, @, [, [[, ^, unary -, unary +, and :) – for example:|> or %>%, and (most often) a new line after – for example:+, and a new line after – for example:The {ARTofR} package is wonderful for creating clean titles, dividers, and block comments for your code. Install the RStudio Addin, or call {ARTofR} functions in your console to generate comments, copy to your clipboard, and paste into your scripts.
I’ve always opted for the console approach:
library(ARTofR)) in your console (rather than in your script / qmd file)A couple dividers that I use often:
xxx_title2("text here") renders as:xxx_divider1("text here") renders as:{ARTofR}):Here’s a short example script demonstrating how I like to use these dividers:
##~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
## Setup ----
##~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
#.........................load libraries.........................
library(tidyverse)
library(palmerpenguins)
#..........................import data...........................
# ~ if you're reading in data, this is a great place to do it ~
##~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
## Data wrangling / cleaning ----
##~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
penguins_wrangled <- penguins |>
# select relevant cols ----
select(species, bill_length_mm, bill_depth_mm, year) |>
# filter for year of interest ----
filter(year == 2009)
##~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
## Data visualization ----
##~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
# histogram of penguin bill lengths in the year 2009 ----
ggplot(penguins, aes(x = bill_length_m, fill = species)) +
geom_histogram()
# scatterplot of penguin bill lengths by bill depths in the year 2009 ----
ggplot(penguins_wrangled, aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm, color = species)) +
geom_point(){tidyverse}